Discover why 50Hz is the standard frequency used in many electrical power systems around the world. Learn the historical, technical, and practical reasons behind the 50Hz power supply standard.
Introduction: What Is 50Hz and Why Does It Matter?
In the world of electrical engineering and power systems, the term "50Hz" refers to the frequency of alternating current (AC) electricity. It means the current changes direction 50 times per second. But have you ever wondered why 50Hz frequency is used in most countries? In this article, we explore the reasons for using 50Hz, its advantages, and how it compares with other frequencies like 60Hz.
Keywords: 50Hz frequency, why 50Hz is used, electrical power systems, alternating current, AC power frequency
1. Historical Reasons for Using 50Hz
The use of 50Hz in power systems dates back to the early 1900s. In Europe, particularly Germany, electrical companies chose 50Hz as a standard due to equipment design and generator efficiency at that time. As German-made electrical equipment was exported globally, many countries adopted 50Hz to ensure compatibility and interoperability. Changing frequency later would have been technically difficult and economically expensive.
Related keywords: history of 50Hz, AC frequency standards, global electrical frequency
2. Technical Considerations and Performance
From a technical perspective, 50Hz offers a balance between system efficiency, motor performance, and power transmission. Key factors include:
Motor speed: At 50Hz, synchronous motors run at predictable speeds. The formula:
Speed = (120 × Frequency) / Number of Poles
helps engineers design standard motor speeds.
Transformer design: 50Hz allows optimal transformer size and cooling for most applications.
Inductive reactance: Lower frequencies like 50Hz reduce losses in long-distance power transmission.
Related keywords: power system design, synchronous motor speed, transformer efficiency, electrical frequency advantages
3. Standardization and Global Usage
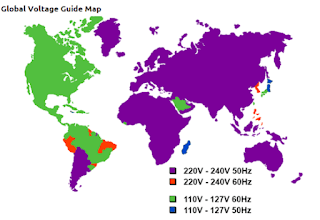
Once 50Hz was chosen by a country or region, changing it became highly impractical. Over time, countries in Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia standardized their grids at 50Hz. Today, over 70% of the world uses 50Hz as the primary power frequency.
Benefits of standardization:
Consistent design of electrical appliances
Easier maintenance of the power grid
Simplified manufacturing and international trade
Related keywords: 50Hz countries list, standard electrical frequency, global power grid
4. Comparison: 50Hz vs 60Hz
Some regions like North America, parts of South America, and a few Asian countries use 60Hz instead. Here’s a brief comparison:
Both frequencies work well, but switching from one to another involves replacing generators, motors, transformers, and entire infrastructures.
Related keywords: 50Hz vs 60Hz, power frequency comparison, AC frequency differences
5. Why Do Most Countries Use 50Hz?
The widespread use of 50Hz is primarily due to:
Historical momentum
Equipment compatibility
Cost of switching frequencies
Efficiency in transmission and design
It’s a practical standard that continues to serve millions of people across continents.
Related keywords: why do we use 50Hz, advantages of 50Hz, electrical grid frequency
Conclusion
Understanding why 50Hz is used in electrical systems is important for both engineers and students. While 60Hz is used in some parts of the world, 50Hz remains the most common AC power frequency due to its historical roots, technical reliability, and economic feasibility.
Whether you're designing an electrical system or studying power distribution, knowing the significance of 50Hz in AC power helps you understand global energy infrastructure.





No comments:
Post a Comment
"Leave us a comment to encourage us."